Amino Acids
An amino acid is a small, organic molecule consisting of an amine group, a carboxylic acid and a side chain specific to each individual amino acid.
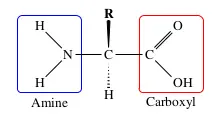
There are twenty naturally occurring (L) amino acids that generally make up the primary structure of a protein. These vary in structure by the side chain R and fall into three general categories;
- hydrophobic amino acids
- charged
- polar
Glycine (Gly), is usually considered by itself owing to the fact its side chain consists simply of a single hydrogen. Sulfur-containing cysteine and secondary amine proline can also be considered special cases.
The exact nature of side chain R—structure, pK
Hydrophobic amino acids
- Alanine
- Valine
- Isoleucine
- Leucine
- Methionine
- Phenylalanine
- Tyrosine
- Tryptophan
Charged amino acids
- Positively Charged
- Arginine
- Histidine
- Lysine
- Negatively Charged
- Aspartic Acid
- Glutamic Acid
Polar amino acids
- Serine
- Threonine
- Asparagine
- Glutamine
Planted: Wednesday, 22 February 2023
Last tended: Monday, 23 June 2025